1. Introduction
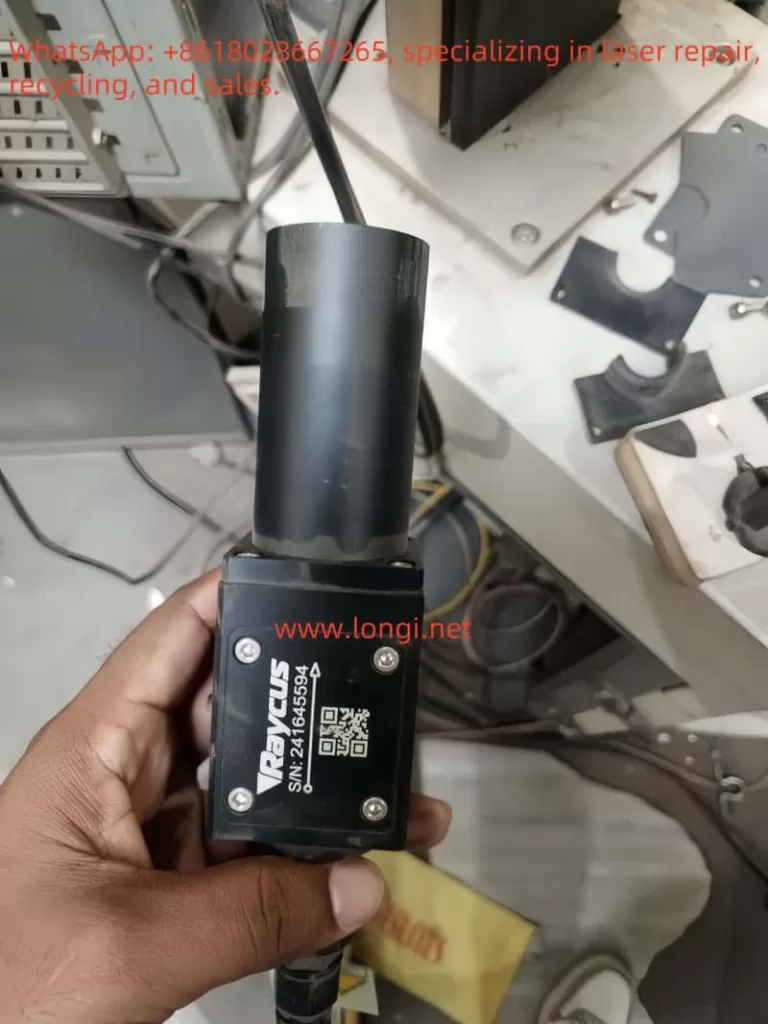
Raycus is one of the leading manufacturers of fiber lasers in China. Its RFL-P series pulsed fiber lasers are widely used in metal marking, welding, cutting, and surface cleaning.
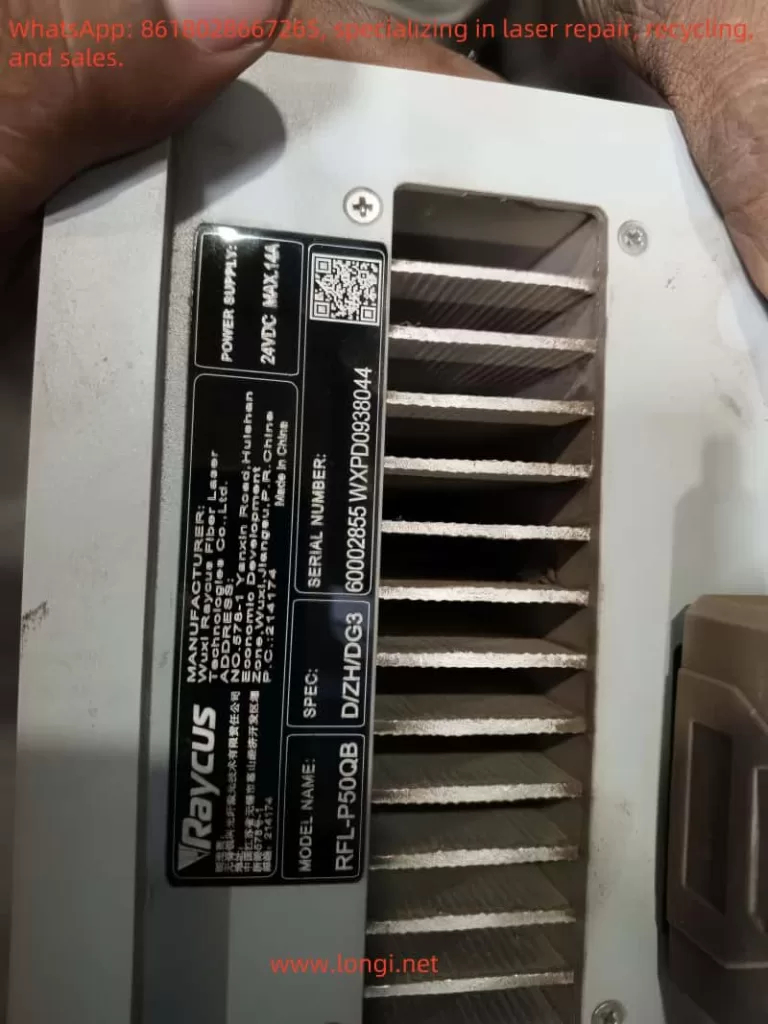
From the nameplate you provided:
- Model: RFL-P50QB
- Output Power: 500W
- Power Supply: 24VDC / Max. 14A
- Structure: Main laser unit + fiber delivery cable + laser output head
In practice, common problems with this equipment are mainly related to power supply, fiber, cooling system, control signals, and the laser module.

2. Common Fault Symptoms
- No laser output at all
- Fans running, but no laser beam emitted.
- Significant power drop
- Originally 500W, now only 100–200W, insufficient for welding or cutting.
- Unstable output
- Power fluctuates, beam spot unstable.
- Alarm indicators or error codes
- Typical errors: over-temperature, fiber fault, module error.
- Output head contamination or damage
- Lens blackened, spot distorted or doubled.

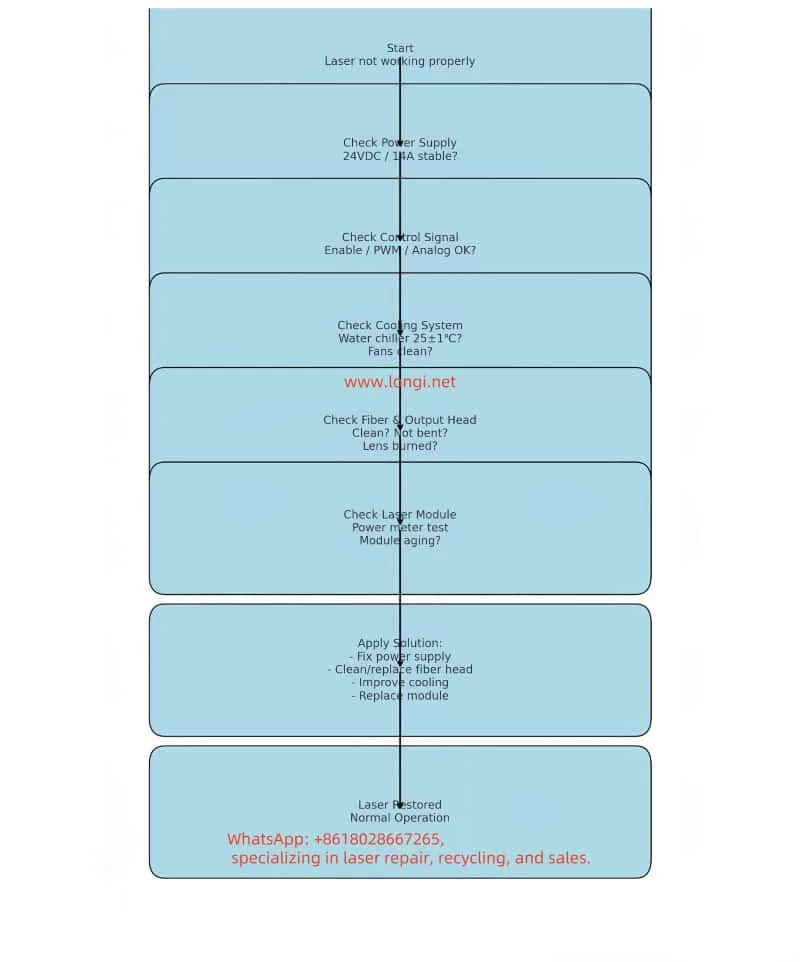
3. Troubleshooting Process
Step 1: Power Supply Check
- Measure the input voltage:
- Rated requirement: 24VDC, max 14A.
- Use a multimeter; voltage must remain within 23.5–24.5V.
- If voltage is too low, the laser cannot start or will output weak power.
- Check power source:
- Ensure power supply capacity is sufficient.
- Tighten loose wiring to avoid overheating.
👉 Key point: Low voltage → no output; ripple noise → unstable laser.
Step 2: Control Signal Check
- Enable signal:
- The laser requires an enable signal from external control (CNC / PLC / marking card).
- Verify connectors are not loose or oxidized.
- PWM / analog signal:
- Power control is typically via PWM or 0–10V input.
- Use oscilloscope or multimeter to confirm correct waveforms.
👉 Key point: Missing signals → no laser; noisy signals → unstable output.
Step 3: Cooling System Check
- Water chiller:
- RFL-P50QB requires water cooling.
- Confirm chiller is running, water temperature at 25 ±1 °C.
- Ensure no bubbles in the pipeline.
- Fans:
- From your photo, the fan intake is dusty. Clean it.
- Weak airflow → overheating alarm.
👉 Key point: Poor cooling → overheating shutdown.
Step 4: Fiber & Output Head Check
- Fiber condition:
- Look for bends, dents, or crushing.
- Severe bending increases loss or causes permanent damage.
- Output head (QBH collimator):
- Inspect lens for black marks or burn spots.
- Clean with isopropyl alcohol (IPA) and lint-free wipes.
- Coupling condition:
- Loose coupling → spot distortion.
👉 Key point: Dirty fiber head → reduced power; damaged fiber → no beam.
Step 5: Laser Module Check
- Drive current:
- If power is normal but no light, module failure is possible.
- Requires factory repair.
- Power measurement:
- Use a power meter to test actual output.
- If significantly lower than rated, the module is aging.
👉 Key point: Aged module → weak power; burnt module → no laser.
4. Common Faults & Solutions
| Symptom | Likely Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| No output | Power supply fault / no enable signal | Check 24V supply, verify control input |
| Power drop | Dirty fiber head / module aging | Clean fiber, replace module |
| Unstable beam | Power ripple / cooling issue | Replace power source, fix chiller |
| Alarm | Overheat / fiber alarm | Check cooling system, fiber endface |
| Distorted spot | Burnt output lens | Replace or repair output head |
5. Maintenance Guidelines
- Keep air vents clean – blow dust with compressed air.
- Replace cooling water regularly – use deionized water or dedicated coolant, change every 3 months.
- Clean fiber connectors – use 99% IPA alcohol and lint-free swabs.
- Avoid frequent plugging/unplugging of fiber heads.
- Stable power supply – use a UPS or voltage stabilizer.
6. Conclusion
The Raycus RFL-P50QB fiber laser is a robust industrial device, but it depends on stable power, proper cooling, clean fiber optics, and correct control signals to function.
From your photos and video, the most likely issues are:
- Dust-clogged fan → overheating
- Dirty or burnt fiber output head → power drop
- Cooling water issues → overheat alarms
👉 Recommended sequence:
- Check power input.
- Verify cooling system.
- Clean fan and fiber head.
- Measure output with power meter.
- If still faulty → send to manufacturer.
