——Practical Analysis Based on HandleException / Default Policy Software Errors
Abstract
The Malvern Mastersizer series of laser particle size analyzers are widely used in laboratories and industrial quality inspection fields. However, abnormalities during software startup are not uncommon. This paper provides an in-depth analysis of the typical error message “An unexpected exception occurred while calling HandleException with policy ‘Default Policy'” that occurs during the startup process. It dissects the issue from the perspectives of the software framework, runtime library dependencies, instrument hardware communication, Aero dry dispersion module, and the Windows system level, offering a complete diagnostic logic, troubleshooting process, and solution ideas for third-party maintenance engineers and equipment managers.
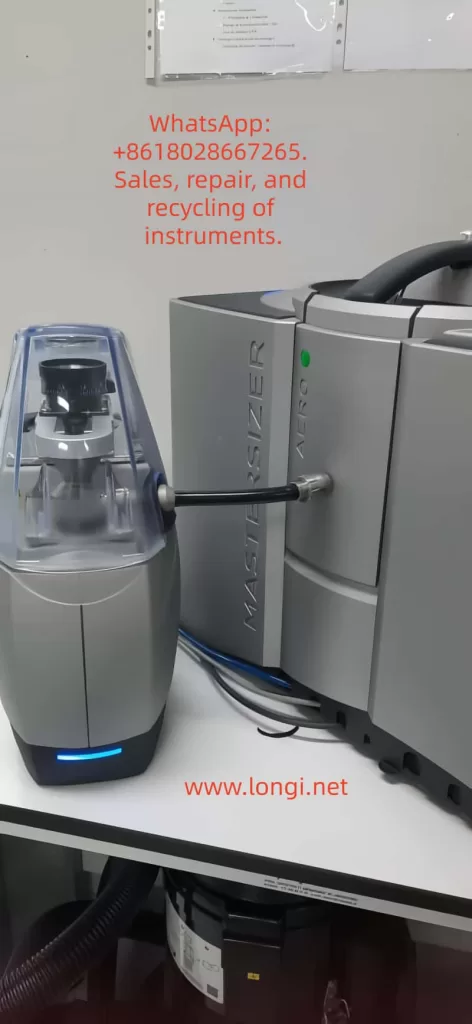

I. Introduction: Why is Malvern Mastersizer prone to startup abnormalities?
The Mastersizer series (including models 2000, 3000, and 3000E) are high-precision particle size testing devices that involve multiple modules such as optical measurement modules, laser optical path systems, expansion units, high-speed data acquisition cards, communication links, and PC software environments. An abnormality in any of these modules can lead to software startup failure. In particular, the Mastersizer 3000 software adopts the Microsoft .NET + Enterprise Library exception management framework, resulting in a complex exception structure that is prone to “HandleException” and “Default Policy” related errors.
II. Reproducing the Fault Phenomenon: What does the error message indicate?
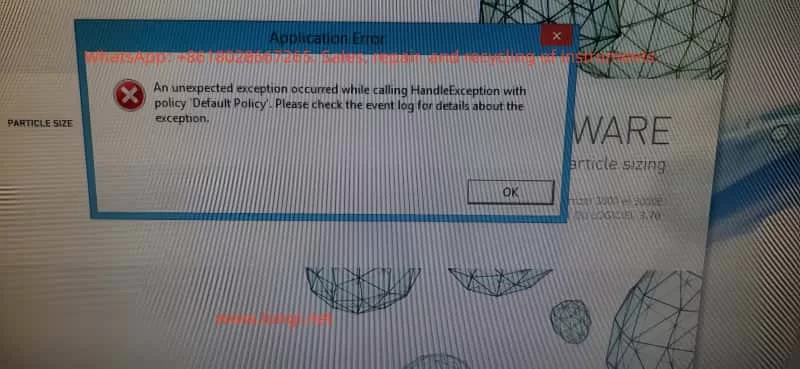
When users start the software, they may see a pop-up window labeled “Application Error” with the message “An unexpected exception occurred while calling HandleException with policy ‘Default Policy’. Please check the event log for details about the exception.” This indicates the following:
- An exception has been captured internally by the software, such as module initialization failure, configuration file reading failure, or device non-response.
- The “Default Policy” that captures the exception has itself encountered an error. The software uses the Microsoft Enterprise Library Exception Handling Block, and when the default policy fails to execute, the software cannot continue to start.
- Such errors do not necessarily directly prove instrument damage; they are more likely to reflect issues such as driver abnormalities, missing software dependencies, or disconnected communication links.
III. Analysis of the Mastersizer Software Startup Process: Understanding the root causes of faults from the source
- Software loading of its dependent DLLs
This includes the .NET Framework, VC++ Runtime, Malvern core module DLLs, and Enterprise Library configuration files, among others. If any DLLs are missing or corrupted, startup abnormalities will occur. - Software reading of configuration files
This involves instrument model information, recently used module configurations, communication ports, laser initialization parameters, and dispersion module configurations. Reading failures will trigger exceptions. - Instrument communication initialization
The communication link for the Mastersizer 3000 may be USB, fiber optic, or RS-232. If the software does not receive a response from the instrument during the initialization stage, an exception will be thrown, especially when there are abnormalities in the Aero dry dispersion module. - Optical system initialization
Failure to turn on the laser drive, non-response from the optical path unit, or no return from the ADC data acquisition card can also lead to software startup failure. - Software UI loading
This stage is unlikely to cause HandleException unless there is damage to system fonts or abnormalities in Windows graphical components.

IV. Typical root causes that may lead to HandleException (ranked by probability)
- Instrument communication failure (highest probability)
Examples include loose or damaged USB cables, use of incompatible USB-HUBs, uninstalled or corrupted USB drivers, and Aero modules that are not powered on or have internal communication board failures. - Corrupted or missing .NET Framework (very common)
The software relies on .NET 3.5 and .NET 4.0/4.5. Windows updates, viruses, or incorrect software uninstallation can damage these components. - Missing VC++ runtime libraries (often overlooked but very critical)
Malvern uses a large number of C++ modules internally, and missing VC++ Runtime libraries will prevent the program from loading. - Corrupted local configuration files of Malvern software
Corruption or formatting errors in files such as software.config, exception.config, and user.config can prevent the Enterprise Library from reading them, triggering Default Policy errors. - Windows permission issues
Examples include the program being unable to write to ProgramData, the software not having administrator privileges, or company IT-installed antivirus systems blocking access to key files. - Host and dispersion hardware issues
These include damage to the Aero fan module, inability of the control board to power on, abnormal sensor output, or interrupted data links.
V. Complete on-site troubleshooting process (standard operating procedure for engineers)
Step 1: Confirm physical connections and power-on status
Check all USB/fiber optic communication cables, unplug and replug them, avoid using USB-HUBs, confirm that both the Mastersizer host and Aero are powered on, and observe whether the LED indicators are normal.
Step 2: Restart the device and computer
The recommended sequence is to close the software, turn off the instrument, restart the computer, turn on the instrument, and then open the software. This is the reset method recommended by Malvern.
Step 3: Check the Windows event log (critical)
Navigate to “Event Viewer → Windows Logs → Application” and search for relevant logs such as Malvern, Mastersizer, .NET Runtime, and Application Error to obtain detailed exception sources.
Step 4: Repair system runtime libraries
Install .NET Framework 3.5, .NET Framework 4.0/4.5, and VC++ 2005/2008/2010/2012/2013 runtime libraries. You can use the Microsoft .NET Repair Tool and the Visual C++ Redistributable Package collection to perform repairs.
Step 5: Reset or delete software configuration files (commonly effective)
Delete the configuration files in the C:\Users\username\AppData\Local\Malvern\ and C:\ProgramData\Malvern\ directories. The software will automatically regenerate them.
Step 6: Reinstall the software (ultimate solution)
This is suitable for situations such as software corruption, abnormal configuration files, missing DLLs, or interference from enterprise antivirus software. A complete reinstallation will almost restore normal operation.
VI. Special case: Abnormalities caused by the Aero dry dispersion module
In the Mastersizer + Aero dry dispersion module combination system, the Aero contains components such as a motor drive, differential pressure sensor, control CPU board, and speed feedback system. If the Aero’s internal hardware is damaged, error messages such as “Unexpected exception” and “Failed to initialize module: Aero” will appear during the software initialization stage. If you observe no indicator lights when the Aero is powered on, no startup action of the suction fan, abnormal fan current, or non-operation of the internal fan on-site, the problem may be concentrated on damage to the Aero control board or fan drive board.
VII. Best advice for engineers
- Confirm communication lines and device power-on status: Re-plug the communication lines and avoid using USB-HUBs.
- Restart the device and computer: Follow the correct restart sequence.
- Check the event log: Obtain detailed exception information.
- Repair the .NET Framework and VC++ Runtime: Ensure that software dependencies are complete.
- Exclude equipment hardware abnormalities (especially Aero): Focus on the fan, control board, and power module.
- Reinstall the software if necessary: Use this as the final solution.
VIII. Conclusion: The essence and solution direction of Mastersizer startup abnormalities
The error “An unexpected exception occurred while calling HandleException with policy ‘Default Policy'” analyzed in this paper is, from a software structure perspective, a secondary exception caused by the failure of the software’s exception handling mechanism. However, the root causes often lie in system runtime libraries, drivers, configuration files, communication links, or abnormal initialization of instrument modules (especially Aero). Through a systematic diagnostic process, almost 100% of the problems can be located.
IX. Appendix: On-site troubleshooting checklist for engineers (printable)
✔ Communication check
- Loose USB/fiber optic cables
- Whether the HUB has been removed
- Whether the instrument is properly powered on
✔ Software environment - .NET Framework 3.5/4.x
- Integrity of VC++ Runtime
- Whether the software has been blocked by enterprise antivirus software
✔ Windows system - Permissions
- Event Viewer
- Whether there are conflicting drivers
✔ Instrument hardware - Aero fan
- Control board
- Internal sensors
- Host power module
✔ Software repair - Delete configuration files
- Reinstall the software
X. Overall Summary
By technically dissecting the startup process of the Malvern Mastersizer particle size analyzer and analyzing the root causes of HandleException / Default Policy errors, it can be concluded that such faults are the result of a comprehensive failure in the coordination of the software, system, drivers, and instrument initialization processes. As long as engineers master the troubleshooting logic proposed in this paper, they can quickly locate and accurately repair most on-site abnormalities.
