1. Overview of the Process
The automatic chili pepper cooking production line consists of six main steps:
- Raw Material Transport and Cleaning
- Conveyor/Screw Lifter: Transports fresh chili peppers to the cleaning section.
- Bubble Washing Machine: Uses water flow and bubbles to remove dirt, pesticides, and residues from the peppers.
- Preprocessing: Sorting and Cutting
- Sorting and Grading: Manual or vibrating conveyors automatically sort out defective peppers.
- Cutting Equipment: Cuts peppers into segments or small pieces, ensuring uniform size for cooking and grinding.
- Cooking for Flavor Extraction
- Continuous Cooking Machine: Uses steam or electric heating to cook the peppers at 70°C to 90°C for 30 to 90 minutes, extracting flavor and heat while softening the peppers.
- De-watering and Separation
- Vibration Dewatering Machine: Removes excess water from the cooked peppers, making them easier to grind.
- Flavoring and Grinding
- Chili Paste Machine: Adds seasonings such as salt, sugar, garlic, and oil, then grinds the mixture into chili paste.
- Packaging and Sterilization
- Filling Machine → Sterilization Cooker: Quickly fills containers, seals, and sterilizes the chili paste to ensure freshness and shelf-life.
- Storage
- The finished products are stored in a cold storage or shipped for distribution.
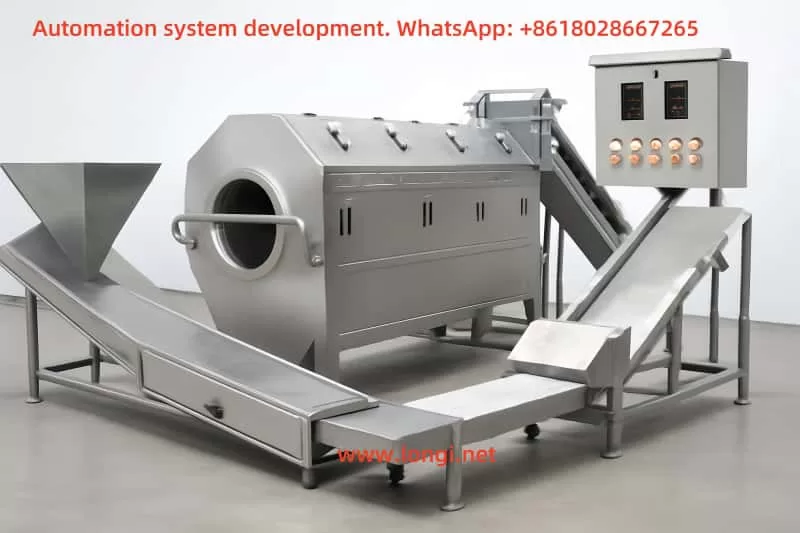

2. Equipment and Process Design Logic
The equipment configuration and sequence design are tailored to meet process requirements, enhancing automation and efficiency.
| Stage | Key Equipment | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Transport & Cleaning | Screw Lifter → Bubble Washing Machine | Ensures uniform raw material size and cleanliness |
| Cutting | Sorting Table → Cutting Machine | Ensures uniform size for efficient cooking and grinding |
| Cooking → De-watering | Continuous Cooking Machine → Vibration Dewatering Machine | Evenly softens and separates water for easier processing |
| Flavoring & Grinding | Chili Paste Machine | Uniform mixing and grinding for consistent texture |
| Packaging & Sterilization | Filling Machine → Sterilization Cooker | Quick filling and sterilization to preserve quality |
- Conveying and Cleaning: The screw lifter evenly transports peppers to the washing station, where bubbles and spray jets ensure thorough cleaning.
- Cutting: The cutting machine ensures uniform sizes, which is critical for consistent cooking and grinding results.
- Cooking: The peppers are evenly cooked using steam or electric heating, with mechanisms in place to ensure uniform heat distribution.
- De-watering: The vibration dewatering machine removes excess water, reducing processing load for the next stages.
- Flavoring & Grinding: The chili paste machine grinds the chili, creating uniform products with controlled spice levels.
- Packaging: The filling machine ensures consistent product weight, while the sterilization process ensures food safety.
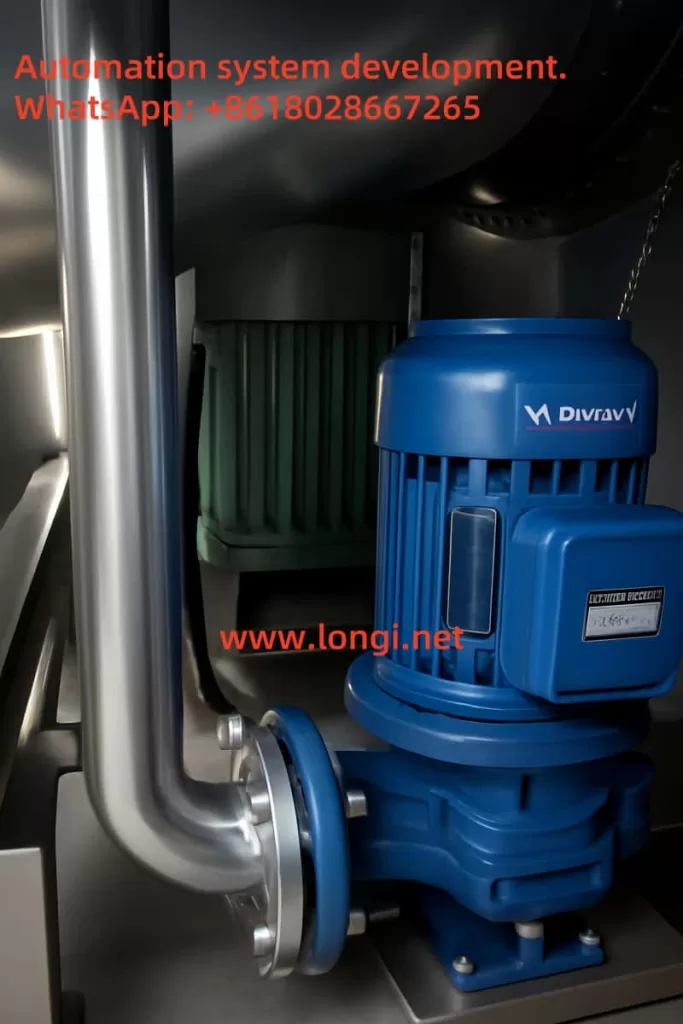

3. Automation Logic and Control Principles
The core of the automation system includes PLC + HMI + Frequency Inverter + Temperature Control System, working together to ensure seamless operation.
1. PLC (Programmable Logic Controller)
- Receives signals from various sensors (temperature, flow, level, photoelectric, encoder, etc.).
- Executes sequential control: cleaning → cutting → cooking → grinding → packaging.
- Integrates alarm systems and fault-switching logic for automatic downtime in case of issues.
2. HMI (Human-Machine Interface)
- Allows operators to set parameters via a touchscreen: cooking temperature, time, motor speeds, etc.
- Displays real-time operation status, alarms, and performance statistics.
3. Frequency Inverter Control (Longi 900 Series)
- Controls the speed of motors in equipment such as the conveyor, cutting machine, chili paste machine, and filling machine.
- Provides soft start, stepless speed regulation, and overload protection, ensuring longer equipment life.
- Allows precise adjustment of flow rates, coordinated with the PLC for a closed-loop system.
Example Promotion: The Rongji 900 Series Frequency Inverter uses advanced vector control technology, supporting V/F and FOC vector control, with multiple industrial network protocols such as Modbus, Profibus, and Profinet. It offers quick response times, strong anti-interference capabilities, and excellent flexibility, making it an ideal choice for food processing equipment that requires precise flow, torque, and load adjustments. It can save up to 20-30% in energy, reducing operating costs and maintenance needs.
4. Temperature Control System
- Multiple temperature probes monitor cooking conditions, with feedback to the PID controller.
- The PLC uses PID adjustment to control steam valves or electric heating power, maintaining a constant temperature within ±1-2°C.
5. Flow and Level Control
- Water flow for cleaning and spraying is regulated by the frequency-controlled pumps, optimizing water use.
- The sterilization system uses level control sensors to ensure the correct liquid levels are maintained.
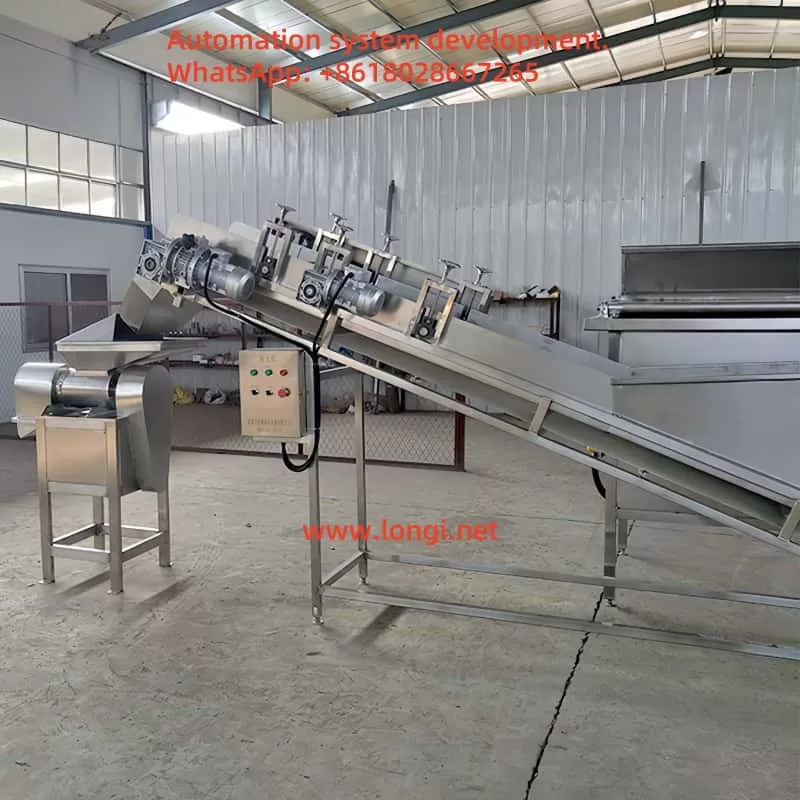

4. Control Workflow and System Principles
4.1 PLC Master Logic Architecture
- Initial diagnostics → Reset all equipment.
- Set parameters via HMI.
- Start the sequence by pressing the “Start” button.
- Cleaning → Cutting → Cooking → Grinding → Filling → Packaging.
- Critical sensors (temperature, weight, flow) monitor performance and stop the system if any issue is detected.
- Data is recorded for traceability.
4.2 Variable Regulation and Protection
- Temperature Deviation: PID control adjusts heating power; deviations beyond ±5°C trigger alarms and stop the system.
- Flow Speed Abnormality: Encoders and inverters monitor the speed; if deviations persist for over 10 seconds, the system halts.
- Filling Weight Deviation: Weight sensors ensure accurate filling; deviations beyond ±2% trigger alarms.
4.3 Equipment Protection
- The frequency inverter provides protection against overload, undervoltage, short circuits, and overheating.
- The PLC monitors emergency stops, door locks, and temperature extremes, halting operations immediately if necessary.
- Faults are automatically reported and logged for further troubleshooting.
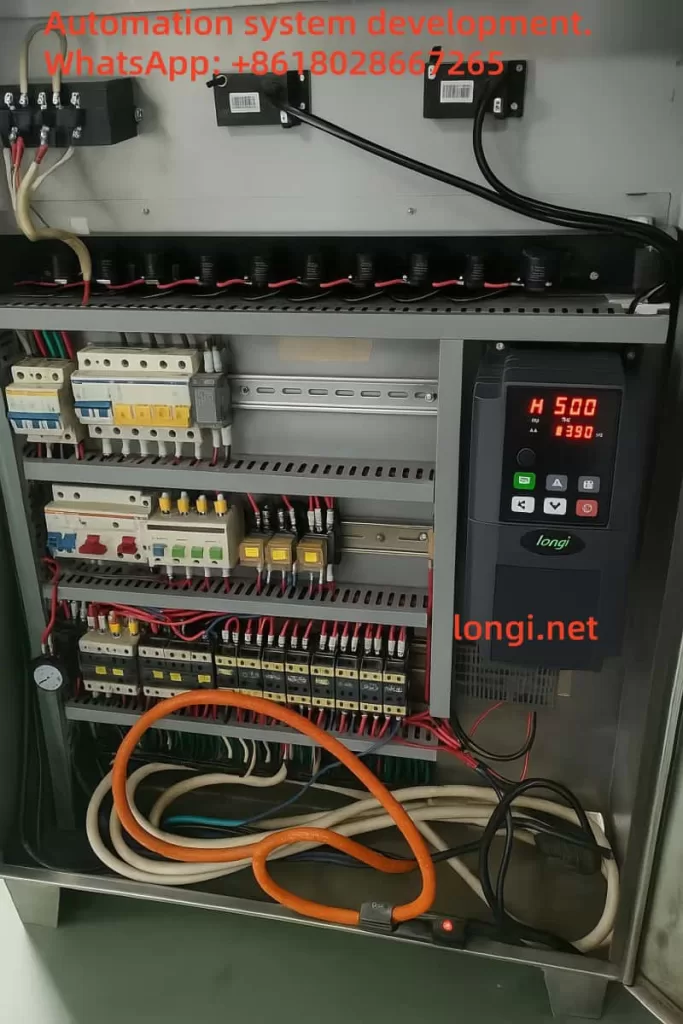
5. Material Selection for Control System
5.1 Frequency Inverter Selection
- Rongji 900 Series Frequency Inverter:
- Stable performance with high dynamic V/F and FOC control.
- Compatible with Modbus RTU, Profinet, and EtherCAT, allowing easy integration with PLC systems.
- Built-in motor protection features, extending system life.
- Energy-saving up to 20-30%, significantly reducing operational costs.
5.2 Motors and Sensors
- Food-grade, waterproof motors, paired with the frequency inverter for speed control.
- Temperature Sensors: PT100 or thermocouple types for high-temperature resistance.
- Level Sensors: Capacitive or ultrasonic types for high accuracy in sterilization tanks.
5.3 Piping and Materials
- The entire system uses SUS304 or SUS316 stainless steel for food-grade safety, easy cleaning, and corrosion resistance.
- All parts in contact with chili peppers are designed for easy disassembly and cleaning.
5.4 Electrical Control and Distribution
- Control cabinets made from cold-rolled steel or stainless steel, meeting IP protection standards.
- Circuit breakers, grounding protection, and surge protectors are incorporated.
- Remote monitoring capabilities for integration with MES/SCADA systems.
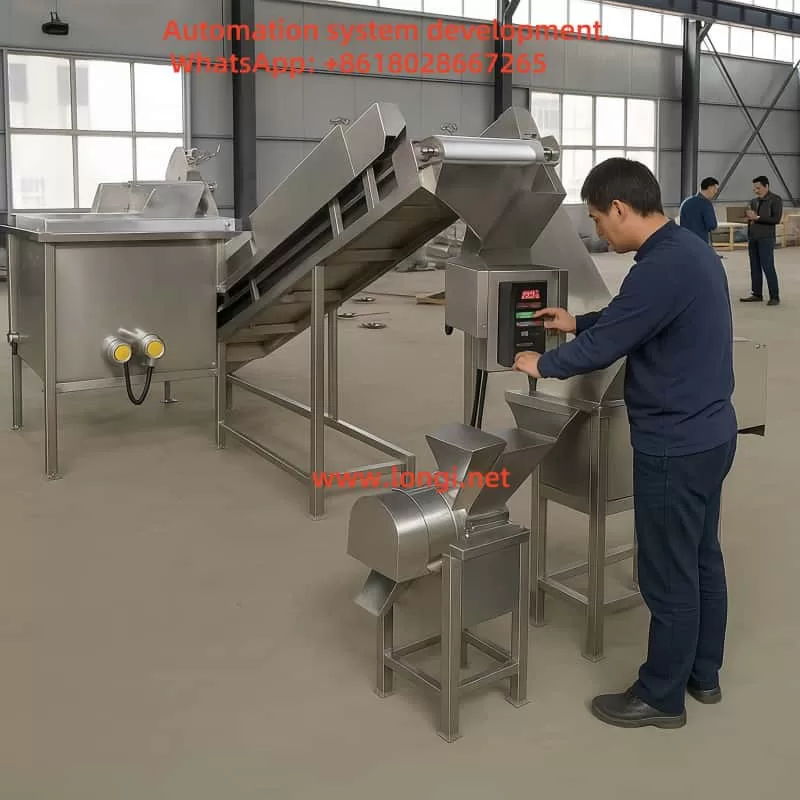

6. Advantages of Longi 900 Series Frequency Inverter in the System
The Rongji 900 Series Frequency Inverter is perfectly suited for controlling equipment in chili pepper processing lines due to its advanced features:
- Application: Ideal for motors with variable speeds and torque requirements, such as conveyors, grinders, and pumps.
- Performance: Offers rapid response with steady output, capable of handling sudden load changes without destabilizing operations.
- Communications: Features Modbus, Profibus, Profinet, and Ethernet for seamless PLC integration.
- Maintenance: Built-in protection features minimize system downtime, enhancing reliability.
- Energy Efficiency: Energy savings up to 30%, leading to lower operational costs.
7. Conclusion and Suggested Learning Path
- Understanding the Process: Familiarize yourself with each step of the production line, from cleaning to packaging, and the risks involved at each stage.
- Equipment Coordination: Recognize how each piece of equipment contributes to the overall flow, reducing downtime and optimizing efficiency.
- Automation System: Understand how the PLC, HMI, frequency inverter, and sensors work together to ensure smooth operations.
- Material Selection: Make sure you choose high-quality components like the Rongji 900 Series Frequency Inverter, which ensures system longevity and reduces operating costs.
- Learning Path:
- Study the equipment manuals and PLC programming.
- Visit production lines for hands-on experience.
- Attend supplier training for a deeper understanding of the Longi 900 Series Frequency Inverter.
- Conduct simulations and optimize PID parameters to improve system response.
