Based on Longi 900 Series Inverter and Mitsubishi FX3U PLC
1. Project Background
Mooncakes are a traditional Chinese delicacy with cultural significance, especially during the Mid-Autumn Festival. With increasing market demand for quality, production capacity, and hygiene standards, traditional manual production methods have become inadequate. Therefore, building an efficient, stable, and intelligent automated mooncake production system is crucial.
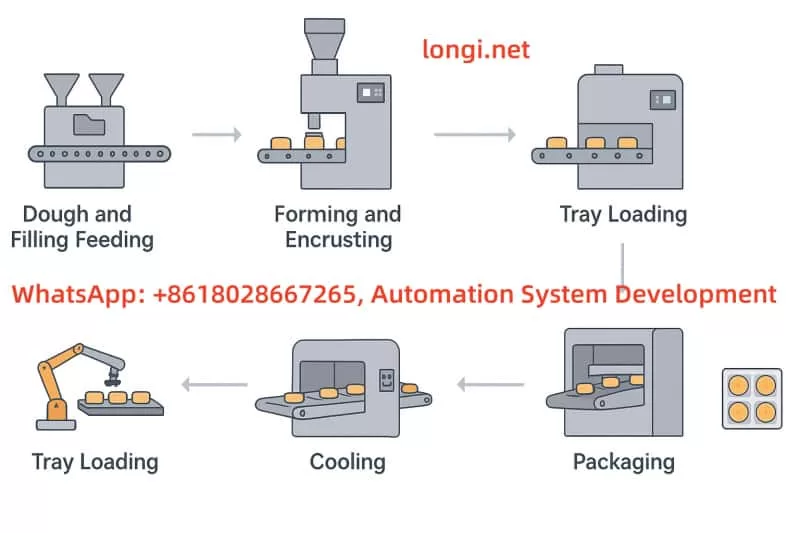
This project proposes an automation control system integrating the Mitsubishi FX3U PLC, Weintek HMI, and Rongji 900 series inverter to manage the entire mooncake manufacturing process—from dough and filling feeding, encrusting, pressing, forming, tray loading, baking, cooling, to final packaging. The system aims to provide a flexible, reliable, and cost-effective solution for small to medium-sized food manufacturers.
2. Detailed Workflow and Production Line Principle
2.1 Overall Operating Principle
The mooncake production line consists of a series of interconnected machines controlled by PLC logic, frequency inverters, and HMI interfaces. Key mechanisms include:
- Synchronization of multiple machines via conveyor belts;
- Detection of workpiece positions using photoelectric sensors;
- Speed control of motors via inverters for precise encrusting, molding, and tray feeding;
- Time-sequenced logic from the PLC ensures no process conflicts;
- Real-time monitoring and parameter setting via HMI.
2.2 Detailed Workflow Breakdown
| Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Raw Material Feeding | Dough and filling are independently fed via hoppers. Dough is delivered using screw or belt feeders, while filling (e.g., lotus paste, egg yolk) is fed by twin-screw or extrusion pumps. |
| 2. Encrusting | An automatic encrusting machine proportionally wraps dough around the filling. Three synchronized feeding systems ensure consistent weight and shape of each mooncake ball. |
| 3. Molding and Pressing | Mooncake balls are first shaped by a vibrating pre-former, then enter the press system. The top-down mold structure creates floral patterns and sets thickness using pneumatic or servo mechanisms. |
| 4. Conveying & Alignment | Molded mooncakes are neatly aligned by guide rails and pushed into baking trays using mechanical pushers. The process is synchronized to avoid overlaps or gaps. |
| 5. Baking | Multi-zone tunnel ovens provide accurate heat distribution (e.g., upper/lower heat). Temperature sensors and alarms ensure safe operation. Advanced models may include vision-based feedback control. |
| 6. Cooling | After baking, mooncakes cool for 5–10 minutes via mesh-belt forced-air systems. Adjustable air speed/direction ensures even cooling, with flipping mechanisms for underside exposure. |
| 7. Inspection | Metal detectors and weight checkers remove defective or foreign-object-containing products. |
| 8. Packaging | Qualified mooncakes are guided by robotic arms or channels into packaging machines for automatic wrapping, sealing, coding, and boxing. The system synchronizes with the conveyor line via PLC signals. |
This line typically supports 50,000 to 200,000 pieces/day with a throughput of 60–120 pieces per minute and easily accommodates various flavors and sizes.
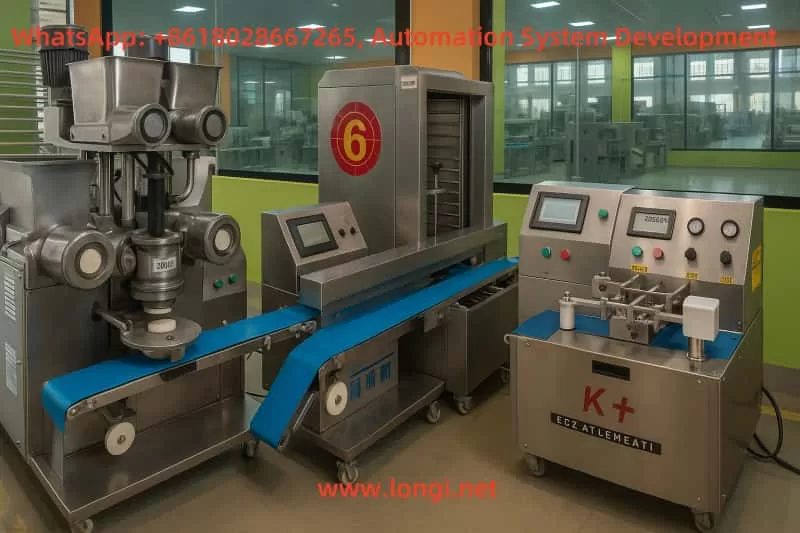

3. System Architecture
3.1 Mitsubishi FX3U PLC
- Manages all I/O signals (e.g., sensors, buttons, alarms);
- Includes main program, interrupt routines, and PID modules for real-time operation;
- MODBUS-compatible for seamless communication with Rongji inverters;
- Expandable with high-speed counting modules for precise positioning.
3.2 Rongji 900 Series Inverter
- Drives dough feeders, encrusters, mold presses, tray pushers, etc.;
- Supports VF and SVC modes for high torque at low speeds;
- Built-in PID for closed-loop control (e.g., pressure in mold presses);
- Multi-speed (F4) support with 8-step preset frequencies;
- Rich I/O terminals for flexible integration.
3.3 Weintek HMI (e.g., TK6071iQ)
- Communicates with PLC via RS-232 or MODBUS-RTU;
- Enables menu control, recipe switching, alarms, and statistics;
- Supports USB recipe import/export and data logging for quality control.
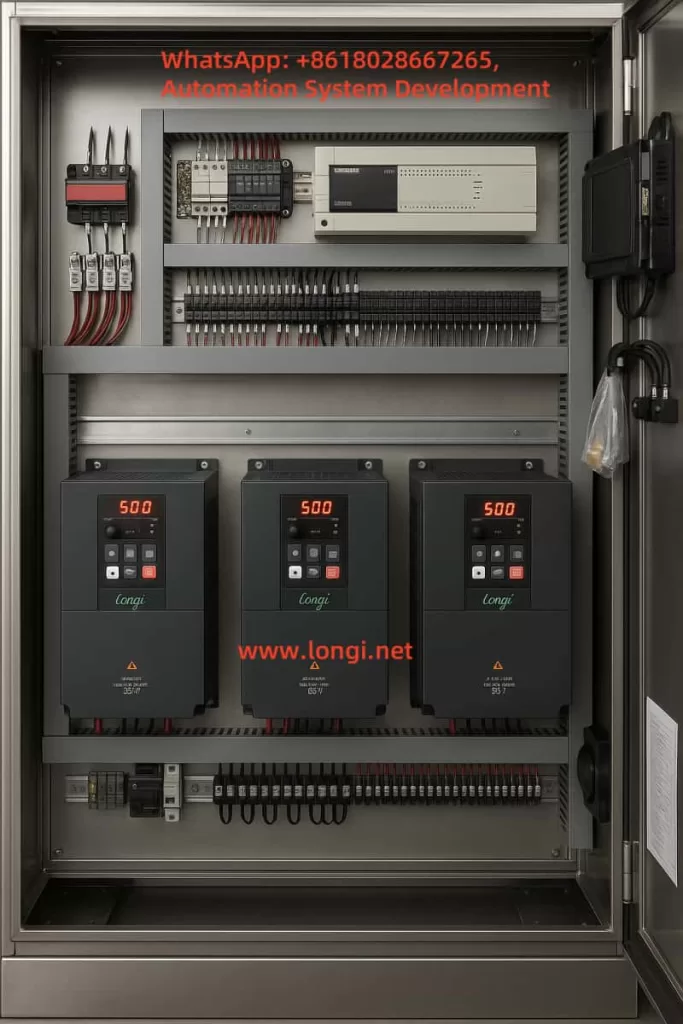

4. Sample Control Logic
Encrusting Module
- DI1: Start signal
- AI1: Speed reference (from HMI or upper system)
- DO1: Completion signal to trigger the next stage
Molding Module
- PLC monitors position sensor and triggers press motor;
- Rongji 900 inverter reads pressure sensor input via AI and uses PID to maintain consistent pressing force.
Tray Loading Module
- PLC controls solenoid valves and pushers based on production rhythm;
- Light sensors detect tray availability;
- System halts and alarms when trays are missing.
5. Advantages of Longi 900 Series Inverter
The longi 900G3 inverters demonstrated the following key strengths in this project:
- Strong Low-Speed Torque: 150% torque at 0.5Hz ensures stable encrusting and precise tray loading;
- Flexible Control Modes: VF and SVC switching adapts to fast feeding and slow pressing tasks;
- Built-in PID: Reduces PLC workload and hardware requirements;
- Compact and Cost-Effective: Ideal for upgrading production lines in small/medium food factories;
- Simple, Reliable Communication: Easy-to-configure MODBUS registers speed up commissioning.
6. Conclusion
This automation system combines Mitsubishi FX3U PLC, Rongji 900 inverters, and Weintek HMI to create a comprehensive, efficient, and stable mooncake production solution. It features flexible parameter settings, smooth operation, high productivity, and easy scalability and maintenance.
As a key drive component, the Longi inverter stands out for its excellent performance and affordability—making it not only ideal for this project, but also highly recommended for other food processing lines such as pastry, frozen food, and beverage packaging.
